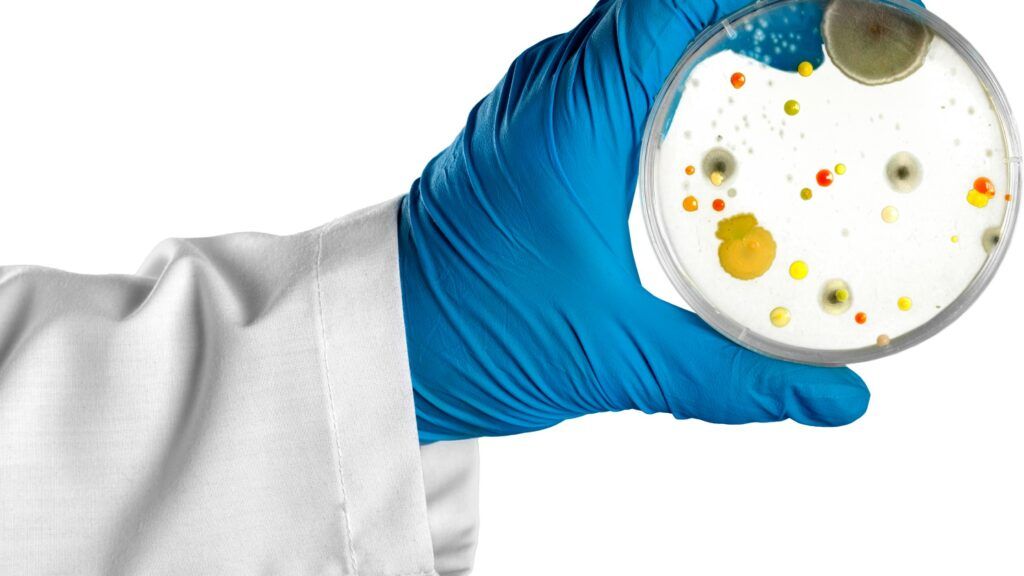
Dehydrated culture media are indispensable tools in microbiology laboratories around the world. Their unique properties make them suitable for a broad range of applications across research, clinical diagnostics, pharmaceutical manufacturing, food safety, and environmental monitoring. This article explores the essential role of these media in microbial identification, characterization, and analysis.
Application of Dehydrated Culture Media
-
Essential Role in Microbiology Labs
Dehydrated culture media provides a convenient, consistent, and readily available source of nutrients to facilitate the growth, isolation, and identification of diverse microorganisms. These media come in powdered form and can be stored at room temperature while retaining their properties for prolonged periods.
When rehydrated, they provide standardized media compositions optimal for the propagation of bacteria, yeasts, molds, viruses, and more. Their defined chemical and physical properties allow for selective isolation of target organisms or differentiation based on biochemical properties.
Microbiologists rely on dehydrated media for a vast array of routine and specialized applications including:
- Pathogen identification through selective and differential plating
- Antibiotic sensitivity testing
- Sterility testing of pharmaceuticals and medical devices
- Water quality monitoring
- Strain typing
- Cell culture propagation and maintenance
By offering convenience, cost-savings, and quality assurance, dehydrated media empowers labs to achieve their objectives with accuracy and efficiency.
-
Ensuring Food Safety & Quality
Preventing foodborne outbreaks is contingent on early detection and control of microbial pathogens and spoilage organisms in food production environments and finished products. Dehydrated culture media is an indispensable tool to enable rapid, reliable pathogen monitoring to protect consumer safety.
Selective media containing inhibitory agents or chromogenic substrates target isolation of key foodborne threats like Salmonella, Listeria, E. coli, and coliforms. Differential media allows further biochemical characterization to pinpoint pathogenic strains. The built-in quality control of these media minimizes batch-to-batch variability, ensuring consistent, accurate results.
Dehydrated media is also widely used in quality control testing by food manufacturers. Testing for indicators of contamination or spoilage during critical control points in processing enables timely corrective actions to prevent substandard products from reaching consumers.
-
Maintaining Pristine Water Quality
Safe drinking water is vital for community health. Dehydrated culture media provides water treatment facilities and testing laboratories the tools to reliably monitor water quality and rapidly detect pathogenic bacteria.
Media containing metabolic indicators enables quantification of total coliforms and E. coli as indicators of fecal contamination. Selective enrichment broths help recover stressed or injured waterborne pathogens. Membrane filtration techniques coupled with differential agars facilitate detection and enumeration of specific pathogens.
The built-in performance controls of dehydrated media give water testing laboratories standardized, reproducible media to generate definitive results on the safety of drinking water. Routine testing and rapid response to pollution enables corrective actions to ensure delivery of clean, potable water.
-
Crucial Role in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Dehydrated culture media is an indispensable component of quality control and good manufacturing practices in pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical facilities. They facilitate sterile production of drugs, vaccines, and biotherapeutics that are uncontaminated by microbial pathogens.
Media is used to validate the sterility of raw materials, monitor environmental controls, perform bioburden testing of products and perform microbial limit testing. Antibiotic-containing media is crucial for isolating and identifying potential contaminants.
Beyond QC applications, dehydrated cell culture media provides defined, consistent conditions for mammalian cell and microbial fermentation processes involved in drug production.
By facilitating compliance with safety regulations, dehydrated media helps pharma companies minimize product recalls and ensure consumer safety, underscoring their importance.
Types of Dehydrated Culture Media
With a diverse range of formulations available, selecting the right dehydrated culture media type is key to successful microbial culturing. This guide explores the properties and applications of various media types tailored to meet specific needs.
-
For Isolating & Identifying Specific Microorganisms
Selective media contains components that inhibit unwanted commensal or background microbes while allowing growth of target organisms. Selective agents like salts, dyes, antibiotics, or antimicrobial chemicals are incorporated into the media.
Common selective media includes MacConkey agar for enteric Gram-negative bacteria, Mannitol Salt Agar for staphylococci, and Sabouraud Dextrose Agar for fungi. These media save time by simplifying isolation procedures.
Selective media enables detection of pathogens from mixed cultures, making them invaluable for clinical diagnostics and food/water testing applications.
-
For Differentiating & Identifying Microorganisms
While selective media isolates target organisms, differential media allows further characterization by leveraging biochemical properties of organisms.
These media contain pH indicators, carbohydrates, or other substrates that induce visible changes when metabolized, differentiating between organisms. E.g. EMB agar differentiates lactose-fermenting E. coli from non-lactose fermenters like Salmonella.
Differential media reduces need for extensive biochemical testing. When used alongside selective media, it enables definitive identification and confirmation of pathogens.
-
To Encourage the Growth of Fastidious Microorganisms
Nutrient compositions of standard media may be insufficient to support the growth of fastidious organisms with complex nutritional needs like pathogens Neisseria and Haemophilus.
Enriched media provides additional nutrients like blood, serum, egg yolk, peptones, and growth factors to meet their fastidious requirements, allowing their isolation from specimens.
Enriched media aids growth and recovery of stressed, slow-growing bacteria. They have crucial applications in diagnostics, food/water testing, and clinical specimen cultivation.
-
To Target & Isolate Specific Bacteria
Incorporating antibiotics into media generates selective pressure for isolation of antibiotic-resistant organisms. Media with antibiotics like nalidixic acid facilitates selective isolation of Gram-negative bacteria from specimens.
Antibiotic-containing media saves time by avoiding overgrowth by commensal antibiotic-sensitive organisms when cultivating drug-resistant pathogens.
They assist in molecular epidemiology studies by enabling selective recovery of organisms that harbor specific resistance genes from mixed populations.
Dehydrated Culture Media: Unveiling the Advantages for Your Lab
Compared to traditional prepared media, dehydrated media offers numerous advantages that enhance efficiency, convenience and quality assurance in the lab.
Some of the key advantages of using dehydrated culture media over traditional culture media includes:
- Reduced preparation time: Simply rehydrate as per manufacturer instructions rather than elaborate media preparation.
- Eliminates batch to batch variation: Consistent quality and performance with standardized formulations.
- Long unrefrigerated shelf life: 2 to 5 years at room temperature cuts storage costs.
- Easy transport: Lightweight, compact packets facilitate shipping and portability.
- Space saving: Requires minimal storage space compared to bulky prepared media.
- Cost-effective: Reduces labor, material, quality control and inventory costs.
- Quality assurance: Rigorous QC testing ensures reliability.
Dehydrated media makes high-quality culture media accessible to labs lacking resources for media preparation or cold storage. Their affordability and ambient temperature storage suits the needs of remote areas or developing countries.
Media designed for automated specimen inoculation and imaging analysis enables high-throughput workflows. Automated preparation reduces variability. Labs can increase testing volumes without compromising accuracy.
Choosing the Ideal Dehydrated Culture Media
Selecting appropriate dehydrated media tailored for the target organism and application is key for successful, reliable outcomes.
- For common aerobic organisms: start with versatile non-selective media like Standard Methods Agar.
- For fastidious bacteria: choose enriched media (with blood/serum).
- For enteric bacteria: use selective media like Hektoen Enteric Agar.
- For fungal cultures: use Sabouraud Dextrose or Potato Dextrose Agar.
- For anaerobes: use pre-reduced media with low redox potential.
Key Factors Choosing Dehydrated Culture Media
- Organism(s) to be cultivated: Different organisms have specific media requirements
- Selective or non-selective: Do you need to isolate target organisms from mixed cultures
- Sample type: Clinical, food, pharmaceutical, or environmental
- Culture conditions: Aerobic or anaerobic? Solid or liquid media?
- Purpose: Diagnostics, screening, research characterization
- Lab skills level: Complex media may increase chance of user errors.
Top Dehydrated Culture Media Manufacturer
MicroMedica Laboratories
 The MML-MCA-01 MacConkey Agar is a selective and differential medium optimized to isolate and differentiate gram-negative enteric bacteria like Enterobacteriaceae. It is manufactured by a trusted company, MicroMedica Laboratories Private Limited. This MacConkey Agar contains bile salts, crystal violet and neutral red to inhibit gram-positives while differentiating lactose fermenters. Recommended for pharmaceutical, clinical, food and dairy testing applications. Formulated with quality ingredients for reliable, consistent results. Requires proper handling by skilled technicians and sterilization before disposal.
The MML-MCA-01 MacConkey Agar is a selective and differential medium optimized to isolate and differentiate gram-negative enteric bacteria like Enterobacteriaceae. It is manufactured by a trusted company, MicroMedica Laboratories Private Limited. This MacConkey Agar contains bile salts, crystal violet and neutral red to inhibit gram-positives while differentiating lactose fermenters. Recommended for pharmaceutical, clinical, food and dairy testing applications. Formulated with quality ingredients for reliable, consistent results. Requires proper handling by skilled technicians and sterilization before disposal.
Dehydrated culture media delivers unmatched convenience, flexibility, and quality assurance for diverse microbiology applications. With their extended shelf life and on-demand preparation, these ready-to-use media enhance productivity and efficiency. Their standardized formulations enable labs to achieve reliable, consistent results. By selecting the right dehydrated media type for your specific needs, you can bring tremendous value to your lab and confidence to your outcomes. Empower your lab workflows with the multitude of benefits offered by dehydrated culture media today.