Suction drains play a vital role in modern medical procedures by facilitating the effective removal of fluids, promoting faster healing, and reducing the risk of post-surgical complications. As healthcare professionals continue to explore innovative solutions, understanding the purpose, types, and proper utilization of suction drains becomes crucial.
In this blog, we will delve into the world of suction drains, exploring their various types, sizes, and benefits. We will uncover the significance of proper placement and care, as well as highlight strategies to manage and prevent complications such as blockages and leaks.
Exploring Different Types of Suction Drains
When it comes to suction drains, the healthcare industry offers a variety of types to cater to different surgical needs and patient conditions. Each type of suction drain has unique features and applications, ensuring optimal fluid removal and promoting patient recovery. Let’s explore some of the different types of suction drains commonly used in medical settings:
- Penrose Drain: The Penrose drain is a flexible, non-collapsible drain made of latex or silicone. It features an open-end design, allowing fluids to drain passively by capillary action. Penrose drains are commonly used for simple surgeries and in situations where minimal drainage is expected. They are cost-effective and easy to use.
- Jackson-Pratt (JP) Drain: The JP drain consists of a perforated tube connected to a bulb reservoir. The tube is inserted into the surgical site, while the bulb collects and holds the drained fluid. Negative pressure is created when the bulb is compressed, facilitating active drainage. JP drains are frequently used in various surgical procedures, such as abdominal or breast surgeries.
- Blake Drain: The Blake drain, also known as a flat drain, is a thin, flat silicone drain with multiple perforations along its length. It is designed for use in areas where a round drain may not be suitable, such as the neck or groin region. Blake drains provide effective drainage and flexibility, allowing them to conform to the contours of the surgical site.
- Hemovac Drain: The Hemovac drain consists of a transparent plastic reservoir connected to a collapsible drainage tube. Negative pressure is created by collapsing the reservoir, allowing active drainage of fluids. Hemovac drains are commonly used in orthopedic surgeries, where a significant amount of fluid is expected to be drained.
- Sump Drain: Sump drains, also known as double-lumen drains, have two separate lumens within a single drain. One lumen actively drains fluid, while the other serves as a vent, preventing the drain from adhering to the surrounding tissues. Sump drains are often used in abdominal or chest surgeries where both active drainage and prevention of tissue adherence are essential.
- Silicone Drains: Silicone drains are made of medical-grade silicone material, providing flexibility and durability. They come in various shapes and sizes, depending on the surgical site and the amount of drainage expected. Silicone drains are commonly used in plastic surgery, cardiovascular procedures, and other complex surgeries.
- Redivac Drain: The Redivac drain is a closed system that consists of a perforated tube connected to a collection chamber. The chamber creates negative pressure, actively suctioning fluid from the surgical site. The closed system reduces the risk of contamination and infection. Redivac drains are frequently used in orthopedic and abdominal surgeries.
- Active Drains: Active drains, such as electronic suction devices or portable pumps, use mechanical suction to actively remove fluid from the surgical site. These drains provide precise control over the suction pressure and allow for constant monitoring of drainage output. Active drains are often used in complex surgeries or cases where a higher level of fluid removal is required.
It’s important to note that the choice of suction drain type depends on various factors, including the surgical procedure, patient condition, expected drainage volume, and surgeon preference. Healthcare professionals carefully assess these factors to determine the most suitable suction drain type for each individual case, ensuring optimal fluid removal and patient comfort.
Understanding Suction Drain Sizes
Suction drains come in different sizes to accommodate various surgical needs and patient conditions. The size of a suction drain refers to the diameter or width of the drain tube. Understanding suction drain sizes is crucial for proper selection and effective fluid drainage. Let’s delve into the different suction drain sizes commonly used in medical settings:
- Small Size: Small-sized suction drains typically have a diameter ranging from 3 to 7 French (Fr). These drains are suitable for procedures requiring minimal drainage, such as small incisions or pediatric surgeries. They are commonly used in delicate surgeries where a larger drain may cause excessive trauma to the tissues.
- Medium Size: Medium-sized suction drains usually have a diameter ranging from 8 to 14 Fr. These drains are versatile and can be utilized in a wide range of surgical procedures, including general surgery, gynecological procedures, and plastic surgery. They offer a balance between drainage capacity and tissue trauma.
- Large Size: Large-sized suction drains have a diameter ranging from 15 to 19 Fr or even larger. These drains are used in surgeries where significant drainage is expected, such as abdominal surgeries or procedures involving large tissue dissections. The larger diameter allows for enhanced fluid removal capacity.
It’s important to note that the appropriate suction drain size is determined by factors such as the expected drainage volume, the surgical site, and the surgeon’s preference. Surgeons carefully assess these factors to select the most suitable drain size for each specific case.
In addition to the diameter, suction drains also come in various lengths. The length of the drain depends on the depth of the surgical site and the amount of drainage expected. Longer drains are used for deeper surgical cavities, ensuring proper placement and effective drainage.
It’s worth mentioning that healthcare professionals have access to a wide range of suction drain sizes, allowing them to tailor the choice of drain to the specific needs of each patient and surgical procedure. By selecting the appropriate size, surgeons can promote optimal fluid drainage, minimize tissue trauma, and contribute to a smooth recovery process for the patient.
The Advantages of Suction Drains
Suction drains offer several advantages in medical procedures, contributing to improved patient outcomes and enhanced post-operative recovery. These drains play a vital role in managing fluid accumulation, promoting wound healing, and reducing the risk of complications. Let’s explore the key advantages of using suction drains:
- Effective Fluid Removal: One of the primary advantages of suction drains is their ability to effectively remove excess fluid and blood from surgical sites. By facilitating efficient drainage, suction drains help prevent the buildup of fluids, which can lead to complications such as seromas, hematomas, or infection. The removal of fluid allows tissues to heal properly and promotes a faster recovery.
- Reduced Infection Risk: Suction drains play a crucial role in minimizing the risk of post-operative infections. By removing fluids that may contain bacteria or pathogens, these drains help create an environment less conducive to infection. Additionally, the continuous drainage provided by suction drains helps keep the surgical site clean and dry, further reducing the risk of contamination and infection.
- Enhanced Wound Healing: Proper drainage is essential for optimal wound healing. Suction drains facilitate the removal of excess fluid, which can impair wound healing by creating tension, preventing tissue approximation, and delaying the formation of granulation tissue. By promoting adequate drainage, suction drains help prevent wound complications and encourage the healing process.
- Prevention of Complications: Suction drains aid in the prevention of various complications associated with fluid accumulation. By minimizing the risk of seromas, hematomas, and abscesses, these drains contribute to a smoother recovery and reduce the need for additional interventions or surgical revisions. By addressing potential complications early on, suction drains promote better patient outcomes.
- Customizable and Versatile: Suction drains come in different sizes and types, offering versatility and customization for various surgical procedures. Surgeons can select the most appropriate drain based on the specific needs of the patient and the surgical site. This flexibility allows for tailored drainage, ensuring optimal results and minimizing patient discomfort.
- Early Detection of Issues: Suction drains also serve as an indicator of any potential issues at the surgical site. By monitoring the drainage output, healthcare professionals can identify changes or abnormalities, such as excessive bleeding or infection, at an early stage. This early detection enables timely intervention and prevents the escalation of complications.
Safe and Effective Suction Drain Removal
Safe and effective suction drain removal is a critical aspect of post-operative care that ensures patient comfort and promotes optimal healing. When the time comes to remove a suction drain, following proper techniques and precautions is essential to minimize the risk of complications and ensure a smooth and successful removal process.
- First and foremost, healthcare professionals must carefully assess the patient’s condition and readiness for drain removal. Signs indicating that it is safe to remove the drain include stable drainage output, the absence of infection or signs of inflammation, and adequate wound healing progress. Once these criteria are met, the drain removal process can commence.
- The medical professional should explain the procedure to the patient and address any worries or queries they may have before starting the treatment. This helps alleviate anxiety and promotes a cooperative environment during the process.
- During the removal, sterile techniques must be followed to prevent infection. The healthcare provider will typically wear sterile gloves and use antiseptic solutions to cleanse the area around the drain insertion site. The drain is then gently and steadily removed, while the patient is instructed to take slow, deep breaths to minimize discomfort.
- After the drain is removed, the insertion site is inspected for any signs of bleeding, infection, or unusual swelling. A sterile dressing is applied to protect the wound and promote continued healing.
- Following the drain removal, patients are advised on post-removal care instructions. This may include proper wound care, such as regular dressing changes and monitoring for any signs of complications. Patients are also informed about the expected drainage patterns and instructed to seek medical attention if they notice any concerning symptoms.
Troubleshooting Suction Drain Blockage
Troubleshooting suction drain blockages is an important skill in medical settings to ensure optimal suction and drainage. Suction drains can occasionally become blocked, impeding the effective removal of fluid and increasing the risk of complications. Understanding common causes of blockage and knowing how to address the issue promptly is essential for maintaining proper drain functionality.
There are several potential causes of suction drain blockage. Blood clots, tissue debris, or fibrin can obstruct the drain tubing, limiting fluid flow. Additionally, kinking or twisting of the tubing, inadequate vacuum pressure, or clogging at the drain’s exit site can also contribute to blockage.
When encountering a blocked suction drain, healthcare professionals should first assess the situation. This involves inspecting the tubing for any visible obstructions and checking the vacuum pressure to ensure it is functioning correctly. Gentle manipulation of the drain tubing can help dislodge small blockages, but care must be taken to avoid dislodging the drain itself.
If gentle manipulation does not resolve the blockage, healthcare professionals may use specific techniques to clear the obstruction. These techniques include flushing the drain with sterile saline solution or using a small, flexible catheter to gently irrigate the tubing. In some cases, mild suction can be applied at the exit site to help dislodge the blockage.
Preventive measures are also important to minimize the risk of suction drain blockage. Regular monitoring of the drain’s functionality, including assessing drainage output and checking for any signs of blockage, can help identify and address issues early on. Proper documentation of drainage characteristics and any interventions taken is crucial for effective patient care.
Suction Drains from Leading Indian Manufacturers
Silicone Wound Drainage System
Angiplast Private Limited, a top-leading manufacturer, offers the Silicone Wound Drainage System, a high-quality medical device supplied worldwide at a reasonable price. This system is made of a silicon-based material and is designed with flat drain tubes to reduce pain during removal. It is individually packed in a medical-grade paper plastic pouch and features a non-return valve that prevents fluid from refluxing. With its reliable performance and innovative design, the Silicone Wound Drainage System ensures effective drainage and patient comfort.
SUR-1016 Closed Wound Suction Unit
Safevac-2
 Disposafe Health and Life Care Ltd. is the leading manufacturer and global supplier of Safevac-2, a suction drain used in medical settings. This closed-wound suction unit features a suction lock and a radio-opaque drainage catheter with smooth holes for efficient drainage. The pierced catheter is designed to reduce trauma to the patient, while the flexible plastic container enables easy activation of the suction.The connecting tube is designed to resist kinking and is free from DEHP, guaranteeing secure and dependable suction.. The Safevac-2 system also includes a sterile, non-pyrogenic, and single-use jar graded for aspiration of 450 ml liquids. It is a trusted solution for effective post-operative drainage.
Disposafe Health and Life Care Ltd. is the leading manufacturer and global supplier of Safevac-2, a suction drain used in medical settings. This closed-wound suction unit features a suction lock and a radio-opaque drainage catheter with smooth holes for efficient drainage. The pierced catheter is designed to reduce trauma to the patient, while the flexible plastic container enables easy activation of the suction.The connecting tube is designed to resist kinking and is free from DEHP, guaranteeing secure and dependable suction.. The Safevac-2 system also includes a sterile, non-pyrogenic, and single-use jar graded for aspiration of 450 ml liquids. It is a trusted solution for effective post-operative drainage.
Closed Wound Suction Unit
The Closed Wound Suction Unit manufactured by Alpha Medicare and Devices Ltd. is a reliable and high-quality medical device. The tube is composed of medical-grade polyvinyl chloride with non-toxic and non-irritant lubricants. The system features a large clamp for controlling negative pressure effectively. The suction catheter is extra smooth and flexible, aiding in smooth wound introduction. The trocar is precisely curved to ensure seamless insertion into the wound. The Closed Wound Suction Unit also includes an X-ray opaque line on the catheter and an international color-coded adopter for easy identification of sizes. Its bellow unit is designed to provide suppleness and maintain negative pressure efficiently.
SURUVAC PRO
SURUVAC PRO, produced by SURU International Pvt. Ltd., is a highly acclaimed and extensively utilized suction drain in India. This closed wound drainage system, equipped with a spring bellow, is specifically designed for effective negative pressure drainage following surgical procedures. It allows the simultaneous use of one or two catheters for efficient drainage. The SURUVAC PRO kit includes a bellow unit with a connector, connecting tube with clamp and “Y” connector, curved needle with matching size catheter, and a spare perforated redon catheter. With its reliable performance and user-friendly design, SURUVAC PRO is a trusted choice for healthcare professionals.
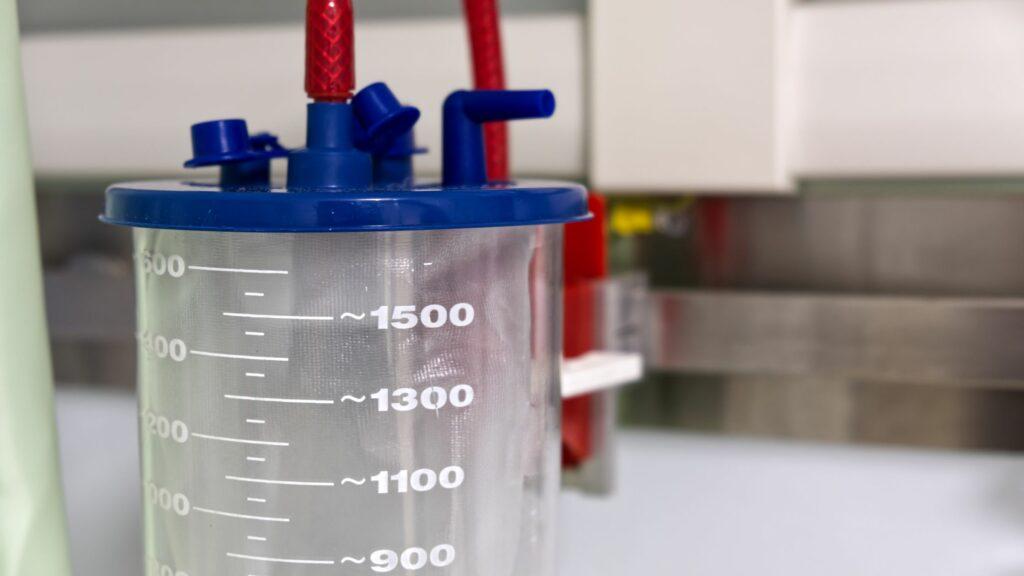
2L Polycarbonate Suction Jar
UnivLabs Technologies Pvt. Ltd., a reputable manufacturer and global supplier, presents the 2L Polycarbonate Suction Jar, a top-notch medical device specifically engineered to provide efficient suction during medical procedures. These suction containers are crafted from long-lasting polycarbonate material and are conveniently calibrated up to 2000 ml, allowing healthcare professionals to assess fluid levels with ease. The jar’s lid is expertly crafted using ABS plastic and features an inlet and outlet port. To ensure optimal safety, the outlet port incorporates a specialized one-way stop valve, effectively preventing any suctioned fluid from backflowing into the machine.
Medzell: Empowering Access to Indian Medical Devices in Emerging Markets
Discover Medzell, a futuristic B2B platform dedicated to promoting Indian medical devices in emerging markets. Uncover how Medzell revolutionizes the procurement process, connecting healthcare providers with reliable suppliers of high-quality suction drains and other essential medical equipment.
Conclusion
Suction drains are indispensable tools in the field of post-operative care and wound management. These devices effectively remove excess fluids from surgical sites, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of complications. Suction drains help minimize the formation of hematomas and seromas by facilitating the drainage of accumulated fluid. They aid in reducing swelling, discomfort, and the risk of infection, thereby enhancing patient comfort and improving overall outcomes.
Proper care and maintenance of suction drains are essential to ensuring their optimal functionality. Healthcare professionals diligently monitor the drainage output, assess the characteristics of the fluid, and promptly address any signs of blockage or complications. Regular dressing changes, sterile techniques, and adherence to prescribed protocols contribute to successful suction drain management.
It is crucial to note that the placement and usage of suction drains should be tailored to each patient and surgical procedure. Surgeons and healthcare teams carefully consider the patient’s individual needs, the type of surgery performed, and the anticipated drainage volume to determine the appropriate drain size, placement location, and duration of usage.
Suction drains have revolutionized post-operative care, allowing for improved wound healing, reduced complications, and enhanced patient recovery. They have become an integral part of surgical procedures across various medical specialties.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect further innovations in suction drain design and functionality. These advancements will likely enhance patient comfort, improve drainage efficiency, and simplify drain management for healthcare professionals.