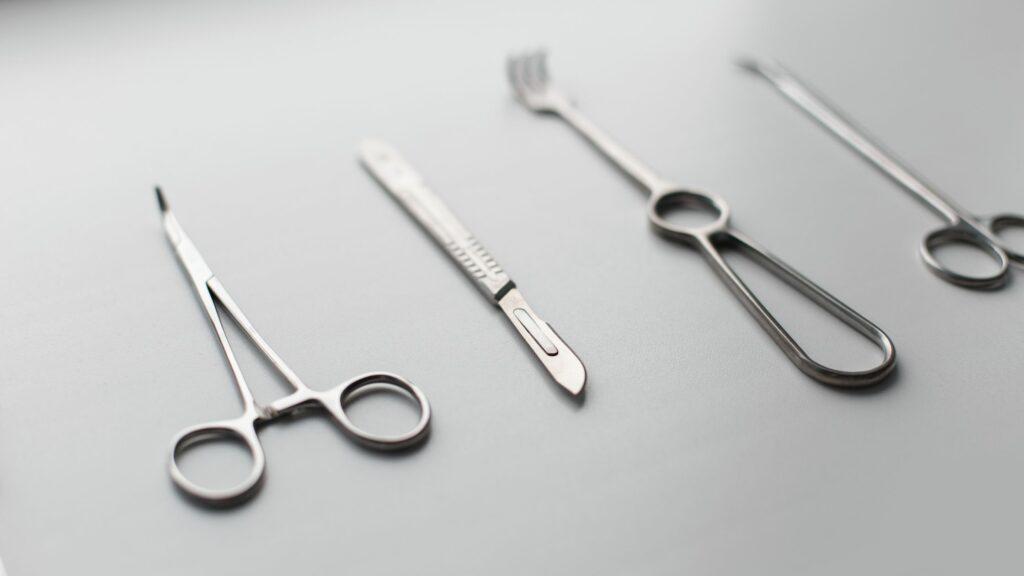
Surgical instruments play a vital role in the field of medicine, enabling healthcare professionals to perform intricate procedures with precision and accuracy. From scalpels to forceps, retractors to scissors, these tools are essential for surgical interventions. Understanding the different types of surgical instruments, their functions, and proper care and maintenance is crucial for healthcare professionals. In this blog, we will explore the various types of surgical instruments, unveil their common names, delve into their functions, discuss sterilization techniques to ensure their cleanliness, and provide essential tips for their care and maintenance. By gaining a deeper understanding of surgical instruments, healthcare professionals can enhance their knowledge, improve communication within the medical field, and uphold the highest standards of patient care.
Exploring the Different Types of Surgical Instruments
When it comes to surgical procedures, a wide array of instruments is utilized to perform precise and delicate tasks. In this section, we will explore the different types of surgical instruments and their specific uses. Understanding these instruments is crucial for healthcare professionals to ensure successful surgical outcomes.
- Cutting Instruments: These instruments are specifically crafted to create incisions or perform excisions during surgical interventions. Instances of such instruments encompass scalpels, scissors, and surgical blades.
- Grasping Instruments: Grasping instruments securely grip and manipulate tissues, organs, or other surgical apparatuses. They furnish surgeons with the essential precision and command over their actions. Illustrations consist of forceps, clamps, and retractors.
- Hemostatic Instruments: Hemostatic instruments find utility in managing and curbing bleeding amid surgical procedures. They contribute to achieving hemostasis and curbing excessive blood loss. Illustrations encompass hemostatic forceps and electrocautery devices.
- Retractors: Retractors are used to hold back tissues or organs, allowing surgeons to access the surgical site and maintain clear visibility. They provide optimal exposure and facilitate the surgical procedure. Examples include handheld retractors and self-retaining retractors.
- Suturing Instruments: These instruments are employed for the purpose of sealing wounds or incisions. They enable accurate positioning of sutures, guaranteeing effective wound sealing and promoting proper healing. Instances of such tools encompass needle holders, suture scissors, and tissue forceps.
- Endoscopic Instruments: These instruments find application in procedures that minimize invasiveness, like laparoscopy or arthroscopy. They grant surgeons access to internal structures through minor incisions, thereby reducing patient trauma. Illustrations comprise trocars, endoscopes, and graspers.
Unveiling the Names of Common Surgical Instruments
In the complex world of surgery, effective communication is vital for seamless teamwork and patient safety. In this section, we will unveil the names of common surgical instruments, enhancing your understanding of their terminology and improving communication within the medical field.
- Scalpel: A scalpel is a precision surgical knife used for making incisions with exceptional control and precision.
- Forceps: Forceps are handheld instruments with two opposing blades used for grasping, manipulating, or extracting tissues or objects.
- Retractor: A retractor is a surgical instrument used to hold back tissues or organs, providing optimal exposure to the surgical site.
- Hemostat: Hemostats, also known as hemostatic forceps, are used to control bleeding by clamping blood vessels during surgical procedures.
- Needle Holder: A needle holder is a specialized instrument used to hold and manipulate surgical needles during suturing.
- Scissors: Surgical scissors come in various shapes and sizes, and they are used for cutting tissues, sutures, or other materials during surgery.
- Speculum: A speculum is a medical instrument used to visualize and access body cavities or openings, such as the vagina or rectum.
- Trocar: A trocar is a sharp-pointed surgical instrument used for puncturing body cavities to allow the insertion of other instruments or drainage tubes.
Ensuring Sterility: Surgical Instrument Sterilization Techniques
Sterility is of utmost importance in surgical procedures to prevent infections and ensure patient safety. In this section, we will explore the various techniques employed to sterilize surgical instruments, safeguarding against the transmission of harmful microorganisms.
- Autoclaving: Autoclaving is a widely used method that utilizes high-pressure steam to sterilize surgical instruments. It effectively kills microorganisms by exposing them to high temperatures.
- Chemical Sterilization: Chemical sterilization involves using disinfectants or sterilizing agents, such as hydrogen peroxide or ethylene oxide gas, to eliminate microorganisms from instruments.
- Dry Heat Sterilization: Dry heat sterilization relies on heat alone to eliminate microorganisms. It involves exposing instruments to high temperatures for a specified period, ensuring their sterility.
- Ultrasonic Cleaning: Ultrasonic cleaning utilizes high-frequency sound waves to remove contaminants from surgical instruments before the sterilization process.
- Sterile Packaging: After sterilization, surgical instruments are often packaged in sterile wraps or containers to maintain their sterility until they are ready for use.
Essential Tips for Surgical Instrument Care and Maintenance
Proper care and maintenance of surgical instruments are essential for their longevity, optimal functionality, and adherence to quality standards in healthcare facilities. In this section, we will explore essential tips for caring and maintaining surgical instruments, ensuring their reliability and performance.
- Cleaning: Thoroughly clean surgical instruments immediately after use, removing any visible debris or organic material. Use enzymatic detergents or specially formulated cleaning solutions.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect surgical instruments for any signs of damage, corrosion, or wear. Replace or repair instruments as needed to maintain their functionality.
- Lubrication: Apply a suitable surgical instrument lubricant to ensure smooth movement and prevent rust or corrosion. Follow manufacturer guidelines for the appropriate lubrication method.
- Sterilization: Follow proper sterilization techniques to ensure the instruments are free from microorganisms. Use validated sterilization processes and maintain accurate sterilization records.
- Storage: Store surgical instruments in a clean and dry environment, protected from dust, humidity, and direct sunlight. Use appropriate storage solutions, such as trays or instrument organizers.
- Handling: Handle surgical instruments with care to avoid dropping or mishandling, which can lead to damage or loss of functionality. Use designated instrument handling techniques.
- Regular Maintenance: Establish a regular maintenance schedule for sharpening, calibration, and servicing of surgical instruments. Follow manufacturer guidelines for maintenance procedures.
By implementing these essential tips for care and maintenance, healthcare professionals can ensure the longevity and optimal performance of surgical instrument, contributing to the delivery of safe and effective surgical care.
Surgical Instrument from Leading India Manufacturer
Stainless Steel Mallet
Introducing the Stainless Steel Mallet, a high-quality surgical instrument manufactured by A.S.F. Universal, one of India’s leading manufacturers and global suppliers of precision medical devices. This mallet is designed to provide exceptional performance and comfort during surgical procedures.
Crafted with precision, the Stainless Steel Mallet features a soft handle that ensures a comfortable grip while withstanding the pressures of surgical applications. This ergonomic design allows surgeons and medical professionals to operate with ease, minimizing fatigue and ensuring precise control.
Unlike many other tenderizers on the market, this Stainless Steel Mallet stands out for its simplicity and outstanding effectiveness. With each well-placed strike, it delivers maximum power, allowing for precise bone manipulation and fracture reduction. The instrument’s superior construction ensures consistent and reliable results.
The Stainless Steel Mallet is designed for convenience and ease of use. Its secure unit features a handle loop, facilitating effortless cleanup and storage. This feature allows for efficient organization in medical settings, ensuring that the instrument is readily accessible and protected when not in use.
With its outstanding features and exceptional craftsmanship, the Stainless Steel Mallet by A.S.F. Universal sets a new standard in surgical instrument technology. It is a reliable and indispensable tool for orthopedic surgeons, enabling them to achieve optimal outcomes with every procedure.
Medzell: Revolutionizing the Future of Medical Device Promotion
Medzell is a futuristic B2B platform that specializes in promoting and connecting healthcare professionals with reliable suppliers of medical devices, including surgical instruments. With a focus on the emerging markets, Medzell aims to facilitate the procurement process and bridge the gap between buyers and sellers in the medical industry.
As an innovative platform, Medzell offers a comprehensive marketplace where medical professionals can explore a wide range of surgical instruments from trusted suppliers.
Through Medzell, buyers gain access to a curated list of reputable suppliers and manufacturers of surgical instruments, ensuring transparency and quality assurance. The platform prioritizes the availability of detailed product information, including specifications, certifications, and pricing, to empower buyers in making informed purchasing decisions.
Medzell’s user-friendly interface and advanced search functionalities make it easy for healthcare professionals to find the precise surgical instruments they require. The platform also offers personalized recommendations based on user preferences, facilitating a seamless and efficient procurement process.
Conclusion
In the world of modern medicine, surgical instruments stand as the silent heroes, playing an indispensable role in ensuring successful outcomes and patient well-being. From the precision of cutting instruments that delicately incise and excise, to the meticulous grasp of tissues by instruments designed for the task, each instrument serves as an extension of a surgeon’s skill and expertise. Hemostatic tools contribute to controlling bleeding, while suturing instruments guarantee the meticulous closure of wounds. In the realm of minimally invasive surgery, endoscopic instruments have revolutionized procedures, minimizing trauma and maximizing results. As technology advances and surgical techniques evolve, these instruments continue to evolve as well, supporting the art and science of surgery. In the hands of skilled professionals, surgical instruments are not just tools, but instruments of hope and healing, shaping the future of medical care one procedure at a time.